Special Education Acronyms:
Definitions for IEP Teams
Every field has a list of commonly used acronyms and for new educators, students and family members attending an Individualized Educational Plan (IEP) meeting for the first time, it may feel a bit like viewing a bowl of alphabet soup. These are a few definitions of special education acronyms and terms to help make IEP meetings and documents easier to understand.
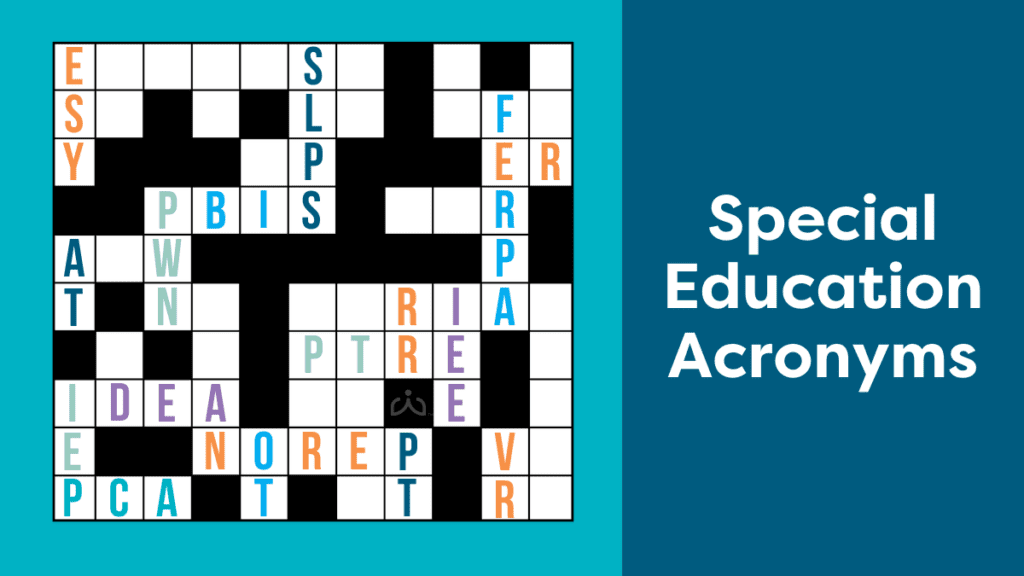
Commonly Encountered Special Education Acronyms and Terms
- 504 (Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973): A civil rights law that requires equal access to education for students with disabilities, who may receive accommodations and services for equitable participation.
- AT (Assistive Technology): A device, equipment, or system that enhances learning. AT includes low- and high-tech tools. An Individualized Education Plan (IEP) Team must consider AT to support access at home, in school, and in the community.
- BIP or PBSP (Behavior Intervention Plan or Positive Behavior Support Plan): Based on a Functional Behavioral Assessment (FBA), a BIP or PBSP is part of an Individualized Education Plan (IEP) and addresses challenging behaviors. The plan outlines strategies that prevent problematic behavior, teach replacement behaviors, and reinforce expected behaviors. It also specifies how to proceed when challenging behavior occurs.
- ER (Evaluation Report): A report that captures the results of a multidisciplinary evaluation that determines eligibility for special education. The ER includes recommendations for families, staff, and other professionals who work with the student.
- ESY (Extended School Year): ESY special education services are provided beyond the school year. Breaks may lead to losing important skills, and it may take students with disabilities longer to recoup these skills. ESY services prevent this by providing services during school breaks.
- FAPE (Free Appropriate Public Education): Part of the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA), FAPE protects the right of a student with a disability to an appropriate education at no cost to parents.
- FBA (Functional Behavioral Assessment): Conducted when behavior hinders learning or that of others, information is gathered about what happens before and after behavior through direct observations and indirect methods (e.g., interviews). Hypothesized functions of the behavior are proposed to develop a Behavior Intervention Plan (BIP) / Positive Behavior Support Plan (PBSP).
- FERPA (Family Education Rights and Privacy Act): A law that protects educational records. It grants parents access to their child’s records, the right to request amendments and control over the disclosure of identifiable information.
- IDEA (Individuals with Disabilities Education Act): A law that stipulates students with disabilities (ages 3 to 21) receive education in public schools. A right to a Free and Appropriate Public Education (FAPE), a comprehensive evaluation, and services that meet the needs of students with disabilities are protected under IDEA. IDEA requires students with disabilities to learn alongside their peers without disabilities to the maximum extent possible.
- IEE (Independent Educational Evaluation): An evaluation by an examiner not employed by a school district. Parents may request an IEE if they disagree with a school’s evaluation.
- IEP (Individualized Education Plan): A person-centered program consisting of individualized services that allow students with disabilities to receive educational benefits.
- LEA Representative (Local Education Agency): An Individualized Education Plan (IEP) Team member who ensures a proposed program meets a student’s needs. They oversee specially designed instruction, are knowledgeable about the general education curriculum, and can commit school resources.
- LRE (Least Restrictive Environment): The requirement that students with disabilities be educated alongside peers without disabilities to the greatest extent possible.
- MAG (Measurable Annual Goal): Outlines what a student is expected to achieve within a year. Each goal targets prioritized academic or functional needs identified in the most recent evaluation report.
- MDE (Multi-Disciplinary Evaluation): Conducted by a team with varying expertise to determine eligibility for special education. The evaluation examines all areas of suspected need. The team may include a general and special education teacher, school psychologist, related service providers, counselor, administrator, and parent.
- OT (Occupational Therapy): OTs and OTAs help learners access classroom and educational experiences through modifications and therapeutic interventions that address fine motor coordination, balance, body awareness, sensory regulation, executive functioning, and attention. Occupational therapists collaborate with IEP Teams to support these areas.
- PBIS (Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports): An evidence-based system that promotes proactive strategies, teaches expected behaviors and uses data-driven decisions to create positive learning communities. PBIS utilizes a tiered system to support all students, target those at risk, and provide interventions for those with intensive needs.
- PCA (Personal Care Assistant): A type of paraprofessional, who assists a student with mobility, hygiene, eating, and other activities, while working under a teacher. Paraprofessionals go by various titles, such as teacher’s aide, one-to-one, or instructional assistant.
- PLAAFP (Present Levels of Academic Achievement and Functional Performance): Also referred to as PLOP (Present Levels of Performance) or PLOEP (Present Levels of Educational Performance), present levels are an overview of current strengths and needs within an Individualized Education Plan (IEP). This section includes information about academic and functional performance derived from assessments, observations, and team input.
- PT (Physical Therapy): Physical therapists assess, treat, and collaborate with Individualized Education Plan (IEP) Teams to improve a student’s mobility and positioning to increase participation, and physical function in academic and extracurricular activities.
- PTE (Permission to Evaluate): An initial evaluation determines eligibility for special education. This involves a variety of assessments, provided at no cost to a parent. A school issues a PTE as a Prior Written Notice (PWN) to seek written consent before an evaluation.
- PTRE (Permission to Reevaluate): Obtains consent before conducting additional assessments as part of a reevaluation to determine continued eligibility for special education. Reevaluations help an Individualized Education Plan (IEP) align with current needs.
- PWN/NOREP (Prior Written Notice/Notice of Recommended Educational Placement): Issued whenever a school proposes or refuses to initiate or change the identification, evaluation, educational placement, or provision of a Free Appropriate Public Education (FAPE). This informs parents and provides the rationale behind decisions regarding their child’s education.
- RR (Reevaluation Report): A reevaluation determines continued eligibility for special education. While reevaluations occur every three years, in certain states, students with intellectual disabilities are reevaluated every two years. Reevaluations are conducted whenever needs warrant it, or if requested by a parent; however, parental consent must be obtained before collecting additional data. The findings are documented in a Reevaluation Report (RR).
- RtI (Response to Intervention): A multi-tiered approach to identify and support students via the delivery of research-based academic and behavioral interventions. The process includes progress monitoring, and if a student does not respond, more intensive support is provided.
- SAS (Supplementary Aids and Services): Aids, services, and other supports provided in the general education setting. These include modifications, assistive technology, and behavioral supports, each meant to remove barriers and maximize access
- SDI (Specially Designed Instruction): Systematic instruction for students with disabilities who may require adjustments to the content, methodology, and delivery of instruction to meet their learning needs.
- SLP (Speech/Language Pathologist): Evaluate, diagnose, and treat students with speech, language, and communication needs. SLPs address speech, language, voice, and fluency to improve academic access and social communication.
- VR (Vocational Rehabilitation): A program that helps individuals with disabilities prepare for, obtain, or maintain a job. This may include career counseling, job placement, goal setting, training, and an Individualized Plan for Employment (IPE). Eligibility necessitates an impairment that impacts employment and the capacity to benefit from VR.
Other Resources for Defining Special Education Terminology
This list isn’t exhaustive but can be a getting started guide. Other resources also include:
Using Special Education Acronyms: Know Your Audience
While educators may be used to using many of the above acronyms, parents, students and those new to education may not. When using an acronym in a document or email, a good practice is to spell out the full term or phrase on the first mention, followed by the acronym in parentheses, and then use the acronym for subsequent mentions. Another practice for IEP meetings or beginning of the year communication with families is to provide them with a list of common acronyms they may encounter.

